In this article we’ll try to explain in simple terms how blockchain works.
Imagine you have a notebook where you keep track of all the things you’ve bought and sold. Every time you make a transaction, you register it in the notebook, along with some details like the date and time, the amount of money exchanged, and who you traded with.
Now imagine that instead of just one notebook, there are thousands of identical notebooks all around the world, and everyone who makes a transaction writes it down in their own notebook. But there’s a catch: before you can add a new transaction to your notebook, you have to solve a really hard math problem. Once you solve the problem, you get to add the transaction to your notebook, and all the other notebooks around the world get updated with your new transaction.
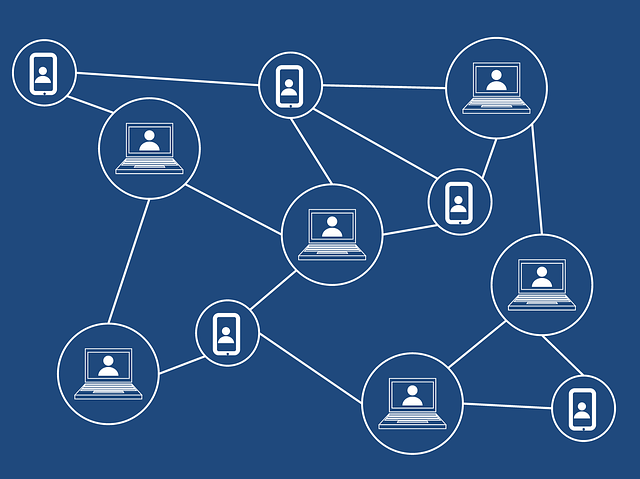
This is kind of like how the blockchain works. Instead of a notebook, there’s a digital ledger that keeps track of all the transactions that happen on the blockchain. And instead of solving a math problem, you have to use your computer to solve a complex cryptographic puzzle. Once you solve the puzzle, you get to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain, and all the other copies of the blockchain around the world get updated with your new block.
A blockchain is essentially a decentralized database or ledger that records transactions and stores them in a way that is difficult to tamper with. Instead of a central authority, like a bank or government, controlling the ledger, the ledger is distributed across a network of computers. Each computer in the network maintains a copy of the blockchain, and all of the copies are updated and synchronized with each other in real-time.
The transactions recorded on the blockchain are grouped together in blocks, and each block is linked to the previous block in the chain, forming a chronological chain of blocks.
One of the key features of this technology is its immutability. Once a block has been added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without invalidating the entire chain. This makes this technology very secure, as any attempt to tamper with the blockchain would be immediately detectable.
This technology is perhaps best known for its use in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, but it has a wide range of other potential applications as well. For example, it could be used to create more transparent and secure supply chains, to manage digital identities, or to facilitate secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a middleman.
The blockchain is really secure because it’s really hard to cheat. If someone tries to add a fraudulent transaction to the blockchain, everyone else will be able to see that it doesn’t match up with the rest of the transactions in the blockchain, and they won’t let it be added. Plus, because there are so many copies of the blockchain, it’s very difficult for any one person or group to manipulate the entire thing.
Images by Pixabay