Virtual reality (VR) is an advanced technology that makes it possible to create an incredibly realistic simulated environment. This environment can be a reproduction of the real world or a completely imaginary universe. The VR experience is immersive: users wear special visors, such as the Oculus Rift or the HTC Vive, which present high-resolution three-dimensional images. These viewers are equipped with motion sensors that track head orientation, allowing users to look around in the virtual environment as if they were physically present.
In addition to visors, Virtual Reality can use sensory gloves or hand controllers, which allow users to interact with the virtual environment in a more natural and intuitive way. These devices can provide haptic feedback, such as vibration, to simulate touch and increase immersion.

On the technical side, Virtual Reality works through advanced software that creates and manages virtual environments. These software are capable of generating 3D graphics in real time, ensuring a smooth and responsive experience. In addition, motion tracking systems and sensors built into input devices detect users’ actions, such as gaze direction or hand movements, and translate them into actions within the virtual environment.
VR has applications in numerous fields, including entertainment, education, vocational training, medicine, architecture and design, and in gaming.
The platforms that support Virtual Reality and the types of viewers available are diverse and constantly evolving.
Here is a general overview.
Main Platforms for VR
PC-Based VR
These platforms require a powerful PC with a high-end graphics card.
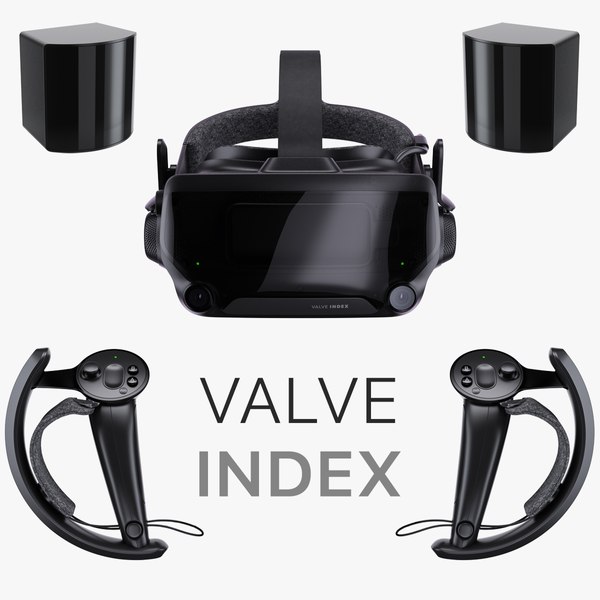
SteamVR – Supports a wide range of VR viewers, including HTC Vive and Valve Index.
Oculus Rift – Initially launched as a PC platform, it is now part of the Meta (formerly Facebook) company.
Console-Based VR
These are VR viewers specifically for game consoles.
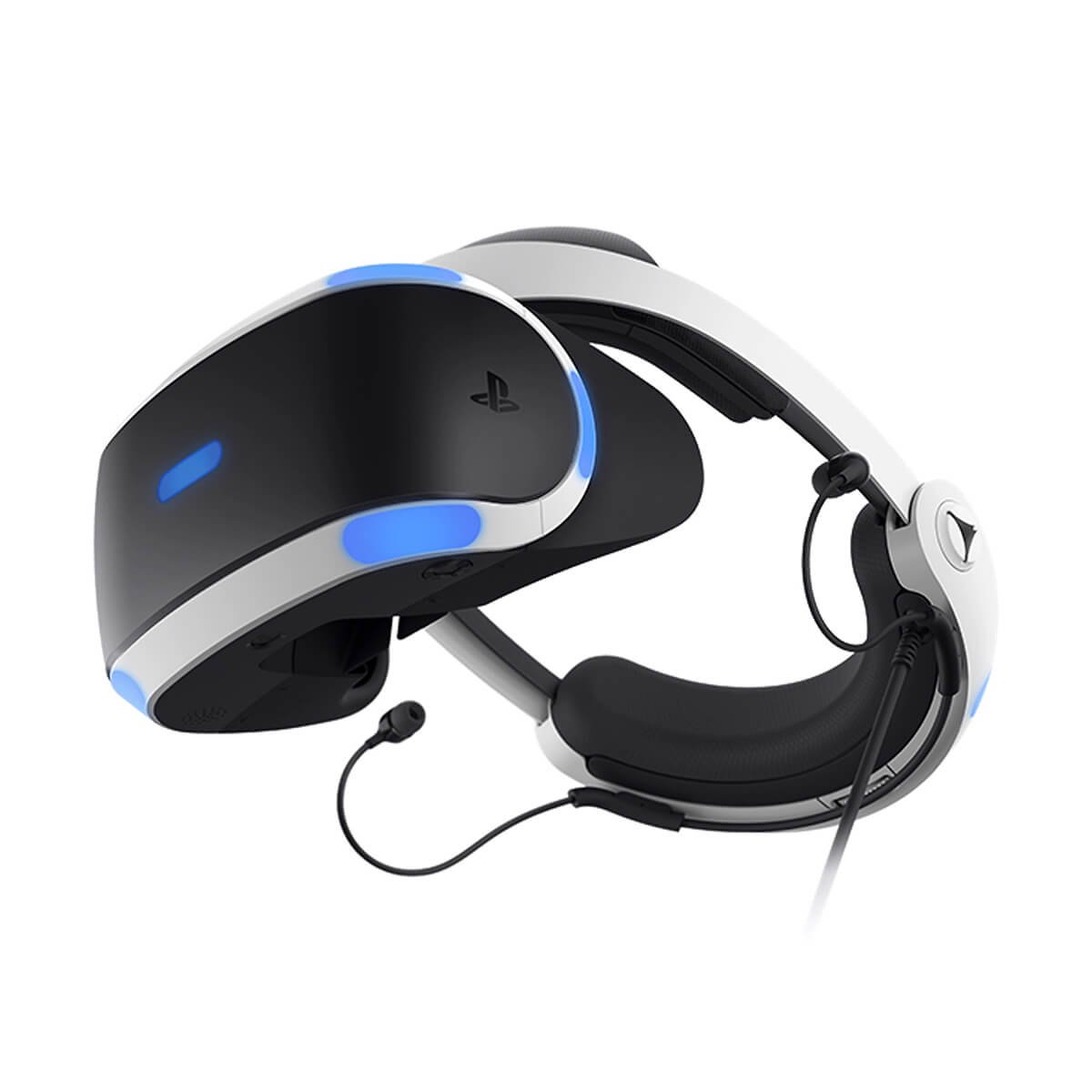
PlayStation VR – Designed for the Sony PlayStation console, it offers virtual reality games and experiences optimized for this platform.
Standalone VR
These devices are standalone, requiring no PC or console to operate.
Oculus Quest – A fully standalone visor that offers a high-quality, wireless VR experience.
Mobile VR
They take advantage of smartphones as a screen and processor.
Samsung Gear VR and Google Daydream – Less powerful than dedicated visors, but offer an affordable introduction to VR.

Types of VR Visors Available
- High-End Visors: Offer the best visual and tracking quality, but require powerful hardware and are more expensive. Examples include Oculus Rift S, HTC Vive Pro, and Valve Index.
- Standalone Visors: Convenient and easy to use, they do not require external hardware. Oculus Quest is the most popular example.
- Console Visors: Like the PlayStation VR, designed to work with a specific game console.
- Mobile VR Visors: They use a smartphone as a screen. They are cheaper but offer a less immersive experience. Examples include the Samsung Gear VR and the Google Cardboard.
Considerations about Visors
- Price: High-end and console viewers tend to be more expensive, while mobile viewers are cheaper.
- Quality: High-end visors offer the best experiences, with precise tracking and high-quality images.
- Accessibility and Portability: Standalone and mobile viewers are easier to set up and use in different environments.
How VR is Applied to Gaming
Virtual Reality has revolutionized the world of gaming, offering an immersive and interactive gaming experience that was unimaginable just a few years ago. Here is how it is being applied to gaming.
Total Immersion
Realistic 3D Environments: VR games transport players into three-dimensional virtual worlds, from fantastical landscapes to realistic reproductions of real environments. This level of visual detail increases immersion, making players feel as if they are truly inside the game.
Intuitive Interaction: Motion controllers allow players to interact with the game environment naturally, as if they were handling real objects. This can include actions such as shooting, grabbing, throwing, and even more complex gestures.
Unique Gaming Experiences
Spatial Exploration: VR allows players to look around and explore the game environment simply by moving their heads, offering a deeper and more intuitive level of exploration than traditional games.
Social Interactions: Some VR games support multiplayer modes, allowing players to interact with others in virtual environments, enhancing the social aspect of gaming.
Simulations and Training
Realistic Simulations: Games in VR can simulate real-world experiences such as flying a plane, driving race cars, or exploring space, offering a level of realism that is difficult to achieve with traditional games.
Training and Practice: VR allows players to practice complex or dangerous tasks in a safe environment, such as military training or medical simulations.
Some of the most popular games that support Virtual Reality include:
- Half-Life: Alyx- A first-person shooter game that redefined the concept of VR games.
- Beat Saber- A rhythm game where players use neon swords to cut musical blocks.
- The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim VR- A VR version of Bethesda’s celebrated role-playing game.
- Superhot VR- A unique action game where time moves only when the player moves.
- Boneworks- An action adventure with very realistic physics.
- No Man’s Sky VR- A space exploration game that offers an immersive VR experience.
- Vader Immortal: A Star Wars VR Series- A series of interactive experiences and adventures set in the Star Wars universe.
- Moss: A graphic adventure combining elements of platforming and puzzles.
- Asgard’s Wrath: An action role-playing game set in a world inspired by Norse mythology.
- Resident Evil 7: Biohazard- A survival horror game that offers an intense virtual reality experience.
- And many more…
Other Areas of VR use
Virtual reality (VR) is also revolutionizing the field of medicine, providing advanced tools for training, treatment and diagnosis. In training, it offers realistic and interactive surgical simulations, enhancing the skills of medical students and healthcare professionals. In patient treatment, VR is used for rehabilitation, aiding in motor and cognitive recovery, and in pain management, offering calming virtual environments.
It is also used in cognitive therapy to treat psychological disorders such as PTSD and phobias. In terms of diagnosis, it enables detailed 3D visualizations that facilitate understanding of complex medical conditions. Finally, VR fosters collaboration among physicians through telemedicine, improving counseling on complex clinical cases.
This emerging technology is therefore making significant improvements in both medical education and patient care.
Advantages and Limitations
Virtual reality offers many advantages, but it also has some challenges and limitations. Here is a summary of the main pros and cons:
Advantages
Immersive Experiences: It offers unprecedented immersion in virtual environments, making them ideal for entertainment, education and training.
Training and Education: Especially useful for training in risky or expensive settings, such as in medicine, aviation and engineering.
Therapy and Rehabilitation: Helps in physical rehabilitation and treatment of psychological disorders by providing a controlled and safe environment.
Safe Exploration: Allows exploring dangerous or inaccessible virtual environments without real risks.
Innovation in Multiple Sectors: Has applications ranging from entertainment to industrial design, from medicine to education.
Limitations
High Costs: Quality hardware and software can be expensive, limiting accessibility for some users or organizations.
Physical Side Effects: Can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea (known as “motion sickness”) and eye strain.
Social Isolation: Prolonged use can lead to social isolation as users are immersed in a completely separate world.
Technical Limitations: Despite rapid developments, there are still limitations in terms of resolution, field of view and motion tracking.
Addiction and Detachment from Reality: As with other immersive technologies, there is a risk of addiction and loss of contact with physical reality.
VR represents a revolutionary technological innovation with a profound and varied impact in many areas, particularly in the fields of medicine and gaming. In healthcare, this technology offers advanced training and education modalities for professionals, improving the quality and effectiveness of surgical and therapeutic procedures.
It opens new frontiers in the treatment of mental and physical disorders, offering innovative rehabilitation methods and nonpharmacological techniques for pain management. In the world of video games, VR has transformed the gaming experience, providing an unprecedented level of immersion and interactivity.
Anyway, this technology is not without its challenges and limitations. High costs, physical side effects, risks of social isolation, and technological dependence are major issues that require attention. The usefulness of a technology in the end is never judged by how it is created, but by its conscious and responsible use.